IdentityServer4深入使用(六)-- 详解资源与客户端的配置
本文内容来自 https://www.jeremyjone.com/835/
开始之前
更多内容,可以查看我的文档:.NET 学习之路-认证中心的配置
正文开始
在 IdentityServer 中,需要我们进行配置的内容,大体分成:IdentityResource、ApiScope、ApiResource 和 Client,它们都是在 IdentityServer4.Models 中定义的。
我们在创建一个 Ids 服务之后,也要首先进行配置初始数据(之前写过的 Config.cs),也就是配置这些内容。
今天要详细梳理一下这些配置,因为它们尤为重要。我们按照官方示例依次梳理:
public static IEnumerable<IdentityResource> IdentityResources => new IdentityResource[] {};
public static IEnumerable<ApiScope> ApiScopes => new ApiScope[] {};
public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> ApiResources => new ApiResource[] {};
public static IEnumerable<Client> Clients => new Client[] {};COPY
IdentityResource
IdentityResource 是预定义的用户身份资源,它包含一些用户的基本信息,如:个人信息、地址、电话号码、邮箱等。
通常,OpenId 和 Profile 是一定给出的,尤其是 OpenId,默认就是强制使用,用户无法取消选择。因为没有这两项信息,就无法确定是哪个用户,而且这些信息本身就是公开的。其余都是可以选项,也都可以调整。
IdentityResource 的作用
IdentityResource 用于确认用户身份,它所包含的内容通常会在 id_token 中,主要是允许哪些资源(claim)可以添加到 id_token 中。尤其是当需要一些自定义授权权限时,这些是必要且灵活的选择。
创建 IdentityResource 内容
public static IEnumerable<IdentityResource> IdentityResources =>
new IdentityResource[]
{
new IdentityResources.OpenId(),
new IdentityResources.Profile(),
new IdentityResources.Email(),
new IdentityResources.Phone(),
new IdentityResources.Address()
};COPY
自定义 IdentityResource 内容
这些是预定义好的五项内容,我们还可以通过自定义的方式进行内容的增加:
new IdentityResource("roles", "角色信息", new List<string> {JwtClaimTypes.Role})COPY
这些身份信息读取用户的 Claim,将其放入 token 中,我们得到的 token 中就会包含这些信息,从而达到获取用户信息的目的。
比如:我们查看预定义的 new IdentityResources.Email() 源码,就会看到其内部已经填写好 JwtClaimTypes.Email 与 JwtClaimType.EmailVerified 两个 claim。当我们的客户端配置了 Email 资源时,获取到的 token 中就会包含这两个 claim。
修改 IdentityResource 内容
框架给我提供了非常方便好用的扩展空间,通过构造函数就可以替换掉我们不希望的内容:
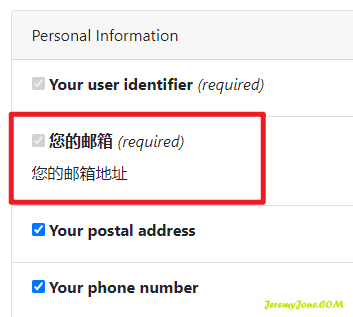
new IdentityResources.Email
{
//Name = IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Email,
DisplayName = "您的邮箱",
Description = "您的邮箱地址",
Required = true,
//Emphasize = true,
UserClaims = new List<string>{ IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Email }
}COPY
这样配置之后,它将显示为中文而不是默认的英文内容,并且它是必须项,用户无法取消选择,同时在获取到的 token 中也没有了默认的 EmailVerified 项。

IdentityResource 的参数
- Enabled
否启用了该资源并且可以请求该资源。默认为 true。
- Name
身份资源的唯一名称。该值对应于客户端授权请求中的 scope 参数的值。
- DisplayName
显示的名称,如在同意界面中将使用此值。
- Description
显示的描述,如在同意界面中将使用此值。
- Required
指定用户是否可以在同意界面中取消选择范围(如果同意界面要实现这样的功能)。false 表示可以取消,true 则为必须。默认为 false。
- Emphasize
指定同意界面是否会强调此范围(如果同意界面要实现此功能)。将此设置用于敏感或重要的作用域。默认为 false。
- ShowInDiscoveryDocument
指定此范围是否显示在发现文档中。默认为 true。
- UserClaims
id_token 中应包含的相关用户声明类型的列表。
ApiScope
ApiScope 顾名思义就是对一个 OAuth API 的范围定义。
版本说明
老版本使用 ApiResource 即可,而新的版本已经开始使用 ApiScope 进行配置。
注意
目前大部分能在网上上找到的博客、帖子,基本上还是老版本的内容,很多视频也是直接使用的 ApiResource,已经不再适用新版本了,需要注意。
ApiScope 的作用
ApiScope 主要用于定义一个 Api 的作用域范围,该范围可以很小。只有当客户端配置的域名与该域名相匹配时才验证通过,否则返回 invalid_scope。
创建 ApiScope
创建一个 ApiScope 十分简单方便:
new ApiScope("mvc", "Mvc Client")COPY
它真的仅仅是一个范围的作用,作用就是控制 OAuth API 的范围。
ApiScope 的参数
- Enabled
是否启用此资源并且可以请求该资源。默认为 true。
- Name
API 的唯一名称。该值用于自检身份验证,并将添加到 access_token 中的 audience 中。
- DisplayName
显示的名称。可以在同意界面中使用该值。
- Description
显示的描述,可以在同意界面中使用该值。
- UserClaims
应包含在 access_token 中的相关用户声明类型的列表。
通过 appsettings.json 配置 ApiScope
使用 AddInMemoryApiScope 扩展方法,可以通过配置文件添加 ApiScope:
"IdentityServer": {
"IssuerUri": "urn:sso.company.com",
"ApiScopes": [
{
"Name": "IdentityServerApi"
},
{
"Name": "resource1.scope1"
},
{
"Name": "resource2.scope1"
},
{
"Name": "scope3"
},
{
"Name": "shared.scope"
},
{
"Name": "transaction",
"DisplayName": "Transaction",
"Description": "A transaction"
}
]
}COPY
然后将配置部分传递给 AddInMemoryApiScopes 方法:
AddInMemoryApiScopes(configuration.GetSection("IdentityServer:ApiScopes"))COPY
ApiResource
ApiResource 定义的是一个 web API 资源。它代表客户端需要访问的功能。通常,它们是基于 HTTP 的终点(API),亦可是消息队列终点或类似的终点。
ApiResource 在新版本中的作用
新版本的 ApiResource 不再适用于客户端的 AllowedScopes 作用域,反而是作为一个更复杂更大的概念而存在。简单来说,每个 API 都可以具有 scope,一些 scope 是针对当前 resource 专属的,而另一些 scope 则是共享与多个 resouce 的。它们的关系好像:
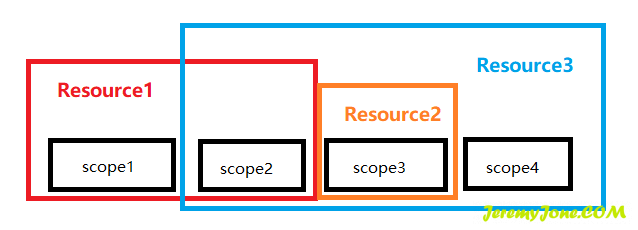
随着 scope 越来越大,需要引入某种命名空间来组织这些作用域,或者将它们分组在一起并获得一些更高层次的结构,比如 access_token 中的 audience claim。此时需要对这些 scope 进行资源整合 -- 将它们配置到一个或多个 ApiResouce 中。
ApiResource 的参数
- Enabled
否启用了该资源并且可以请求该资源。默认为 true。
- Name
API 的唯一名称。该值用于自检身份验证,并将添加到 access_token 中的 audience 中。
- DisplayName
显示的名称。可以在同意界面中使用该值。
- Description
显示的描述,可以在同意界面中使用该值。
- ApiSecrets
用于自检端点。该 API 可以使用 API 名称和密码进行自检身份验证。
- AllowedAccessTokenSigningAlgorithms
access_token 允许的签名算法列表。如果为空,将使用服务器默认的签名算法。
- UserClaims
应包含在 access_token 中的相关用户声明类型的列表。
- Scopes
API Scope 名称列表。
定义 ApiResource
在定义 ApiResource 之前,需要首先定义一些 Scope,比如:
public static IEnumerable<ApiScope> GetApiScopes()
{
return new List<ApiScope>
{
// invoice API specific scopes
new ApiScope(name: "invoice.read", displayName: "Reads your invoices."),
new ApiScope(name: "invoice.pay", displayName: "Pays your invoices."),
// customer API specific scopes
new ApiScope(name: "customer.read", displayName: "Reads you customers information."),
new ApiScope(name: "customer.contact", displayName: "Allows contacting one of your customers."),
// shared scope
new ApiScope(name: "manage", displayName: "Provides administrative access to invoice and customer data.")
};
}COPY
现在,我们使用 ApiResource 对上面的作用域定义两个逻辑 API:
public static readonly IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources()
{
return new List<ApiResource>
{
new ApiResource("invoice", "Invoice API")
{
Scopes = { "invoice.read", "invoice.pay", "manage" }
},
new ApiResource("customer", "Customer API")
{
Scopes = { "customer.read", "customer.contact", "manage" }
}
};
}COPY
如上,我们就有了两个 ApiResource,它的功能如下:
- 支持 Jwt 的 aud 声明,audience 值就是 ApiResource 的值
- 支持在所有包含的范围内添加普通用户声明
- 支持通过添加 ApiSecret 进行自检
- 支持为资源配置 access_token 的签名算法
通过 appsettings.json 配置 ApiResource
与 ApiScope 一样,ApiResource 同样可以通过配置文件添加:
"IdentityServer": {
"IssuerUri": "urn:sso.company.com",
"ApiResources": [
{
"Name": "resource1",
"DisplayName": "Resource #1",
"Scopes": [
"resource1.scope1",
"shared.scope"
]
},
{
"Name": "resource2",
"DisplayName": "Resource #2",
"UserClaims": [
"name",
"email"
],
"Scopes": [
"resource2.scope1",
"shared.scope"
]
}
]
}COPY
然后将配置部分通过 AddInMemoryApiResource 方法添加:
AddInMemoryApiResources(configuration.GetSection("IdentityServer:ApiResources"))COPY
如何使用 ApiResource
根据上面的功能介绍,总结下来就是在客户端配置对应的 Scope,比如 "customer.read",系统会自动查找对应的资源名称,如果存在,就给声明中的 audience 字段添加 ApiResource 的名称。
如果添加了多个 Scope,比如 "customer.read" 与 "invoice.read",则会在 audience 字段中添加多个值 -- 即: ["customer", "invoice"]。
同时要注意,如果使用内存模式,在添加到服务时,要先添加 AddInMemoryApiScopes(Config.ApiScopes) 再添加 AddInMemoryApiResources(Config.ApiResources),否则永远找不到 ApiResource。
何时使用 ApiResource
对于对于需要进行资源认证的客户端,需要将所对应的 Scope 配置到 Resource 中,并且设置资源的秘钥。客户端验证名称和秘钥即可。
比如前后端分离,前端通过 oidc-client 获取到 token,后端服务器使用该方法可以验证 token。
Client
这个很好理解,就是客户端,一条配置就是一个客户端。客户端就是一个可以从身份服务器请求令牌的应用、网站等程序。
定义 Client
定义 Client 时,通常会有以下通用设置:
- 唯一的 Client Id
- 一个秘钥(需要的话)
- 授权类型
- 重定向 URI
- 访问范围列表
服务器访问服务器的客户端 ClientCredentials
该情况不存在用户的交互行为,仅仅是服务器之间的通信,属于高度可信的通信状态。比如服务集群中的两台服务器之间的数据交互行为。这种情况使用 ClientCredentials 类型即可。大体配置如下:
public static IEnumerable<Client> Clients =>
new []
{
new Client
{
// 客户端 Id
ClientId = "jz",
// 客户端获取 Token
ClientSecrets = new[] {new Secret("www.jeremyjone.com".Sha256()) },
// 使用客户端认证
AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ClientCredentials,
// 允许访问的 Api
AllowedScopes = new[] { "api.jeremyjone.com" }
}
};COPY
交互客户端 Code
该情况通常是具有交互行为的 MVC 的 Web 应用程序,或者移动应用程序。
它包含两个物理操作:
authorization:所有的交互行为(登录、同意等)都通过浏览器发生 front-channel 的步骤中,此步骤生成一个 authorization_code 表示 font-channel 的结果。
code:通过 back-channel 的步骤将获取到的 authorization_code 与请求令牌交换,同时机密客户端需要验证身份。
这个流程具有不错的安全性,但还是可能泄露个人数据,所以需要使用 PKCE 秘钥模式,它在 .net core 中默认开启。对于 PKCE,详情请阅读此处。
大体配置如下:
new Client
{
ClientId = "interactive",
ClientSecrets = { new Secret("49C1A7E1-0C79-4A89-A3D6-A37998FB86B0".Sha256()) },
AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.Code,
RedirectUris = { "http://localhost:44300/signin-oidc" },
PostLogoutRedirectUris = { "http://localhost:44300/signout-callback-oidc" },
RequireConsent = true,
AllowOfflineAccess = true,
AllowedScopes = {
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Email,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile
}
}COPY
密码模式 Password
该情况应用于绝对信任的站点交互,因为第三方客户端会收集用户的密码信息。一般情况下不推荐使用该方式,但不排除一些绝对信任的情况,如公司内部不同部门之间登录的情况等。
大体配置如下:
new Client
{
ClientId = "pwd client",
ClientSecrets = { new Secret("pwd client secret".Sha256()) },
AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassword,
AllowedScopes =
{
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Email,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Address
}
}COPY
隐匿模式 Implicit
该模式相对来说比较常用吧,随着前后端分离,前端使用的情况还是比较多的。
该模式安全性比密码方式高很多,用户直接在身份服务器登录,客户端不需要知道用户密码。缺陷是前端需要保存对应的 token,而考虑到 token 的安全性,可以适当缩短有效时间。
大体的配置方式:
new Client
{
ClientId = "implicit client",
ClientName = "Implicit 客户端",
ClientUri = "http://localhost:8080",
AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.Implicit,
AllowAccessTokensViaBrowser = true,
RequireConsent = true,
AccessTokenLifetime = 60 * 5,
AlwaysIncludeUserClaimsInIdToken = true,
RedirectUris =
{
"http://localhost:8080/callback",
"http://localhost:8080/callback-refresh"
},
PostLogoutRedirectUris =
{
"http://localhost:8080/logout"
},
AllowedCorsOrigins =
{
"http://localhost:8080"
},
AllowedScopes =
{
"api.read", "api.create", "api.update", "api.delete", "mvc.delete",
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Email
}
}COPY
混合模式 Hybrid
这个混合是指特定的组合了 Implicit 与 Code 的两种方式,它也是使用比较多的模式。对比单纯的 Code 模式,它结合了隐匿模式,更加适合 Web 应用程序、原生桌面以及移动应用程序。
大体的配置方式:
new Client
{
ClientId = "hybrid client",
ClientName = "Hybrid 客户端",
ClientSecrets = {new Secret("hybrid client secret".Sha256())},
AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.Hybrid,
AccessTokenType = AccessTokenType.Reference,
RequireConsent = true,
RequirePkce = false,
AllowAccessTokensViaBrowser = true,
RedirectUris = {"http://localhost:7100/signin-oidc"},
PostLogoutRedirectUris = {"http://localhost:7100/signout-callback-oidc"},
AllowOfflineAccess = true,
AlwaysIncludeUserClaimsInIdToken = true,
AllowedScopes =
{
"mvc.read", "mvc.create", "mvc.update", "mvc.delete",
"api.read", "api.create", "api.update", "api.delete",
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Email,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Address,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Phone,
IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile,
"roles",
}
}COPY
更多
关于本节的具体代码,可以查看代码示例。有完整的多端,可以直接运行测试。
本作品采用 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议 进行许可
全部评论